7+ Free Body Diagram Acceleration
Web If the system is accelerating it is also a good idea to indicate the accelerations direction also somewhere on the diagram. According to Newtons 2nd law Fnet external force M acceleration F net external force M acceleration.

5 7 Drawing Free Body Diagrams University Physics Volume 1
Web Staying stationaryat rest means that the box has 0 velocity and 0 acceleration.

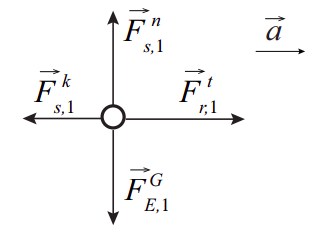
. We know the acceleration is 0ms2 so we can substitute it to get ΣFm 0 which multiplies to. Web Draw and label your acceleration vector off to the side of the dot -- not touching the dot. Web The figure below shows as an example a free-body diagram for a block in the presence of both a nonzero acceleration and a friction force.
What Is the Purpose of a Free Body Diagram. Study free body diagram examples and how they are drawn and examine how to write free body diagram equations. Free body diagrams are tools that are used to visualise the force and moments applied to a body and to calculate the resulting reactions in many types of mechanics problems.
Using several examples The Physics Classroom shows how to calculate the acceleration using a. Once a free-body diagram is drawn Newtons laws of motion can be applied to solve the problem. Web A Free Body Diagram represents the forces acting on an object without considering the objects surrounding environment.
Subtract the forces in the negative direction from those in the positive direction. Web 2 votes Flag Abosh Upadhyaya 5 years ago It is because when you split forces you have to use the Pythagorean theorem or hypotenuse2 side2 side2. Web Equipped with information about the forces acting upon an object and the mass of the object the acceleration can be calculated.
Decide which direction is positive and which is negative. Web Engage the simulation below to predict qualitatively how an external force will affect the speed and direction of an objects motion. Getting a Handle on Torque.
Explain the effects with the help of a free-body diagram. Explain how the graphs relate to one another. Web We also reproduced the vector for the acceleration we drew the vector for the acceleration using a thicker arrow to indicate that it has a different dimension.
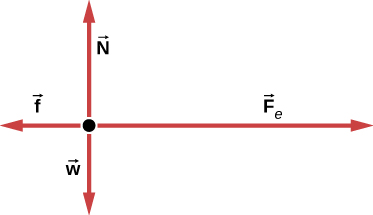
Web Bodies other than the free body diagram. Web Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. Here is an example of a free body diagram for a block of cheese resting on a table see figure 2 below.
Web Christian Miller View bio How to Identify Free-Body Diagrams for Accelerating Objects Step 1. Identify the forces their directions and magnitudes exerted on the analyzed object. Web In what little remains of this chapter we will focus on the easy part.
Velocity and acceleration vectors. If you square the hypotenuse you get 202 which equals 400 N. Linear and Angular Velocity.
Use free-body diagrams to draw position velocity acceleration and force graphs and vice versa. Use free-body diagrams to draw position velocity acceleration and force graphs and vice versa. 1 with the friction force adjusted so as to be compatible with a nonzero acceleration to the right.
Newtons first law is applied if the body is in equilibrium whereas Newtons second law is applied if the body is accelerating. Web Forces and Free-Body Diagrams in Circular Motion. Web Remember in free body diagrams you only care about the forces acting on one of the the objects in your system.
That is F net 0 F net 0 or Newtons second law if the body is accelerating unbalanced force. That is F net 0 F net 0 or Newtons second law if the body is accelerating unbalanced force. A free-body diagram is a useful means of describing and analyzing all the forces that act on a body to determine equilibrium according to Newtons first law.
It helps in visualizing and understanding the various forces acting on an object making it easier to analyze and solve problems related to equilibrium motion and interactions between objects. If there is no acceleration then write a 0. So if were looking at only the block whats going on.
On block M M gravitational force Mg M g is acting downwards tension T T upwards and net acceleration is downwards. Web Once we have drawn an accurate free-body diagram we can apply Newtons first law if the body is in equilibrium balanced forces. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
That is F net 0 F net 0. Newtons 2nd law says that the sum of the forces equals mass times acceleration ΣFma. Web Explain the effects with the help of a free-body diagram.
That is F net 0 F net 0. Given a Free Body Diagram use it to find an unknown force or unknown forces andor use it to find the acceleration of the object. Explain how the graphs relate to one another.
Here F F and a are vectors means acceleration will be in direction of net force. If the problem asks for it use the net force to find mass or acceleration. Given a scenario or a graph sketch all four graphs.
Web Draw a separate free-body diagram for each object in the problem. Web Learn how to make a free body diagram in physics. Web Once we have drawn an accurate free-body diagram we can apply Newtons first law if the body is in equilibrium balanced forces.
Web We must draw a separate free-body diagram for each object in the problem. The diagram includes all the forces even gravity and the normal force. Were going to assume that the block is on earth were assuming that its stationary.
We also reproduced the angle θ in the free-body diagram as this is helpful once the free-body diagram is used with Newtons Second Law. In this case the hypotenuse is 20 N and the two sides are 10 N and 10sqrt 3. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit.
Web Draw a free body diagram of the object. Angular Position and Displacement. How to Make a.
The figure below shows as an example a free-body diagram for a block in the presence of both a nonzero acceleration and a friction force.

Collision Induced Unfolding Tandem Ms Bottom Up Proteomics And Interactomics For Identification Of Protein Complexes In Native Surface Mass Spectrometry Journal Of The American Society For Mass Spectrometry
15 5 Free Body Diagrams Physics Libretexts

Force Free Body Diagrams Physics Don T Memorise Youtube

Falling Bodies Ppt

Fig 2 42 Given Below Shows A Velocity Time Graph For A Car Starting From Rest The Graph Has Three Parts Ab Bc And Cd I State How Is The Distance Travelled In Any Part
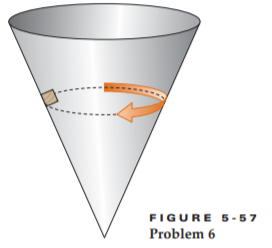
Solved If It Is Started Properly On The Frictionless Inside Surface Of A 1 Answer Transtutors

Free Body Diagram Rules Equations Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
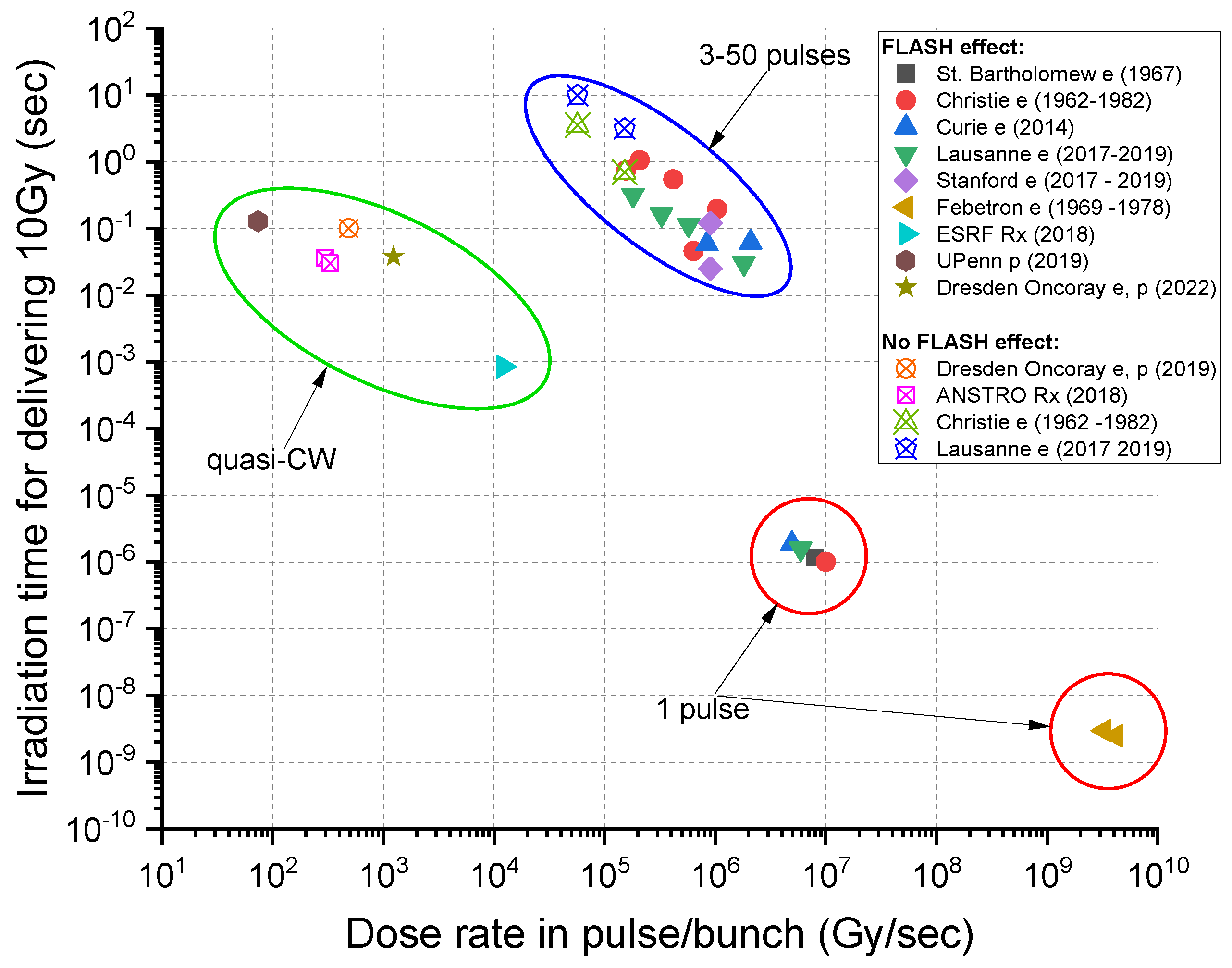
Applied Sciences Free Full Text Transformative Technology For Flash Radiation Therapy

5 7 Drawing Free Body Diagrams University Physics Volume 1
In Free Body Diagram Calculations Why Do We Subtract Tension T From Weight Mg Or Vice Versa To Calculate Acceleration Quora

5 7 Drawing Free Body Diagrams University Physics Volume 1
5 7 Drawing Free Body Diagrams University Physics Volume 1
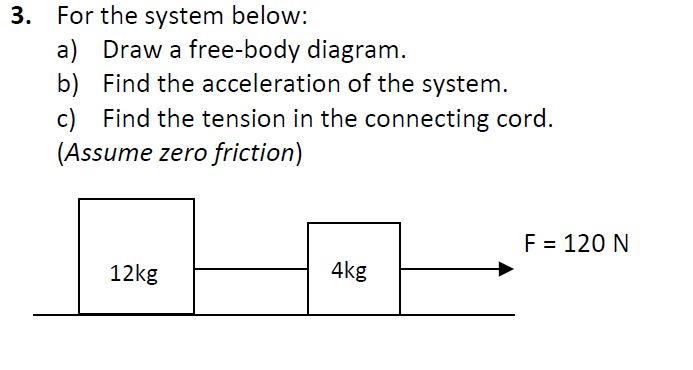
Solved For The System Below A Draw A Free Body Diagram B Chegg Com
Acceleration Gcse Physics Study Mind

Draw A Free Body Diagram For The Following Object In A Uniform Circular Motion Indicate The Forces That Cause Centripetal Acceleration In The Following Case A Car Turning A Curve On A

4 6 Problem Solving Strategies Bcit Physics 0312 Textbook
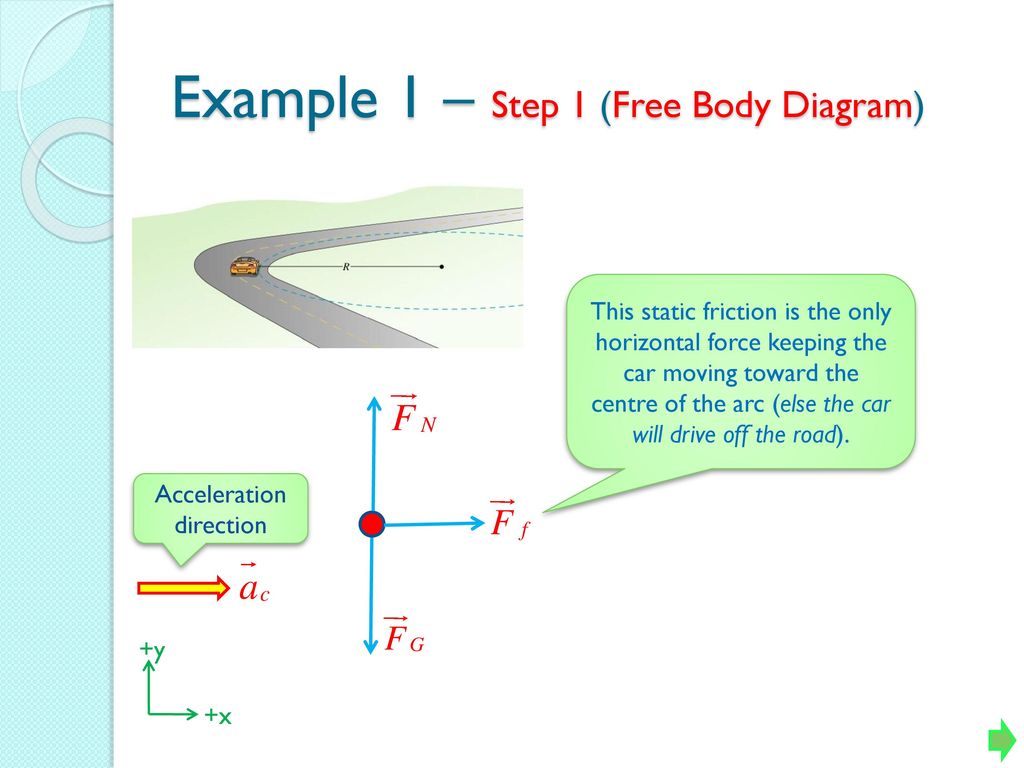
Centripetal Acceleration Ppt Download